In the first of this series we discussed the worship of Artemis and other gods that were prevalent at Ephesus. None of these problems are limited to a single group of Christians but I will often use one of the churches as an illustration.
The second problem faced by the Christians of Asia Minor was Emperor worship. It is common to hear a lot of talk about the persecution of the early Christians, but the term is not used in the Apocalypse. Instead we find the terms trial (Rev. 3:16) and suffer (Rev. 2:10) and tribulation (Rev. 1:9; 2:9,10,22; 7:14). The term tribulation implies pressure brought upon the Christians. We may think of this as persecution but let us not get hung up on that particular term. In my tour notebooks for this area I have included a chart showing the Ten Major Persecutions under the Roman Empire typically listed in works on church history. Here below is that simple list. Nero’s persecution seems to have been limited to Rome. By the time we reach Diocletian we see a more widespread situation. In A.D. 305 Diocletian ordered that all church buildings be burned along with all books and Bibles of the church.
1. Nero (A.D. 64–67).
2. Domitian (A.D. 81–96).
3. Trajan (A.D. 98–117).
4. Hadrian (A.D. 117–138).
5. Marcus Aurelius (A.D. 161–180).
6. Septimus Severus (A.D. 193–211).
7. Maximinus the Thracian (A.D. 235–236).
8. Decius (A.D. 249–251).
9. Valerian (A.D. 257–260).
10. Diocletian (A.D. 303–311).

Ten major persecutions against Christians by Roman emperors. Photo: Ferrelljenkins.blog.
If one understands the Babylon of the book of Revelation (14:8; 16:19; 17-18) to be the Roman Empire then we see the “soon” of passages like 1:1, 3:11, et al. to include this entire period. Certainly the same or similar situations face Christians of all ages.
A bit of background of the situation in Asia Minor might be helpful to some readers. The next section comes from my Studies in the Book of Revelation which includes a chapter on Emperor Worship.
The Roman Empire was made up of many smaller nations. Rome accepted all of the “gods” and the Pantheon in Rome was erected so that all these “gods” could be worshiped. Later, the rulers were often worshiped by all citizens. The worship of kings was common in the eastern portion of the Roman empire. About three hundred years before Christ the Attalid Kingdom was set up in Asia Minor. These Attalid kings, many of them bearing the name Attalus, were worshiped as gods. At Pergamum one may see the ruins of the heroon, outside the citadel gate, which served as a sanctuary of the heroized kings.
Attalus III, who died in 133 BC, bequeathed all the movable assets of his empire to the Romans. “This was misinterpreted as meaning all his possessions, including his whole kingdom. Thus, the Romans inherited a country of 66,750 square miles with the most beautiful cities of Asia Minor” (Cosmades, Nothing Beside Remains, 36). This territory served as an excellent buffer between Rome and the Seleucid empire of Syria and later the Parthians. This explains how Rome came to have power in Asia Minor. Emperor worship was easily adopted by the people of this region.
Christians could not worship the emperor and were considered atheists by Empire standards. The Christians were not persecuted for serving Christ, but for not worshiping the emperor. The cities of Asia Minor vied for the honor of erecting a temple to the emperor. Pergamum won this honor as early as 29 B.C. (cf. Rev. 2:13). When the Christians were persecuted some of them were willing to serve the Emperor but others were willing to die. It cost something to be a Christian then. (Studies in the Book of Revelation, p. 5.)
⇒ This book is available from the Florida College Bookstore here. Search for the title of the book or the author’s name.)
One of the significant things to see during a visit to the ruins of ancient Ephesus is called Domitian Square. There we see the platform with steps leading to the top where the Temple of Domitian, or Temple of the Flavian Emperors once stood.
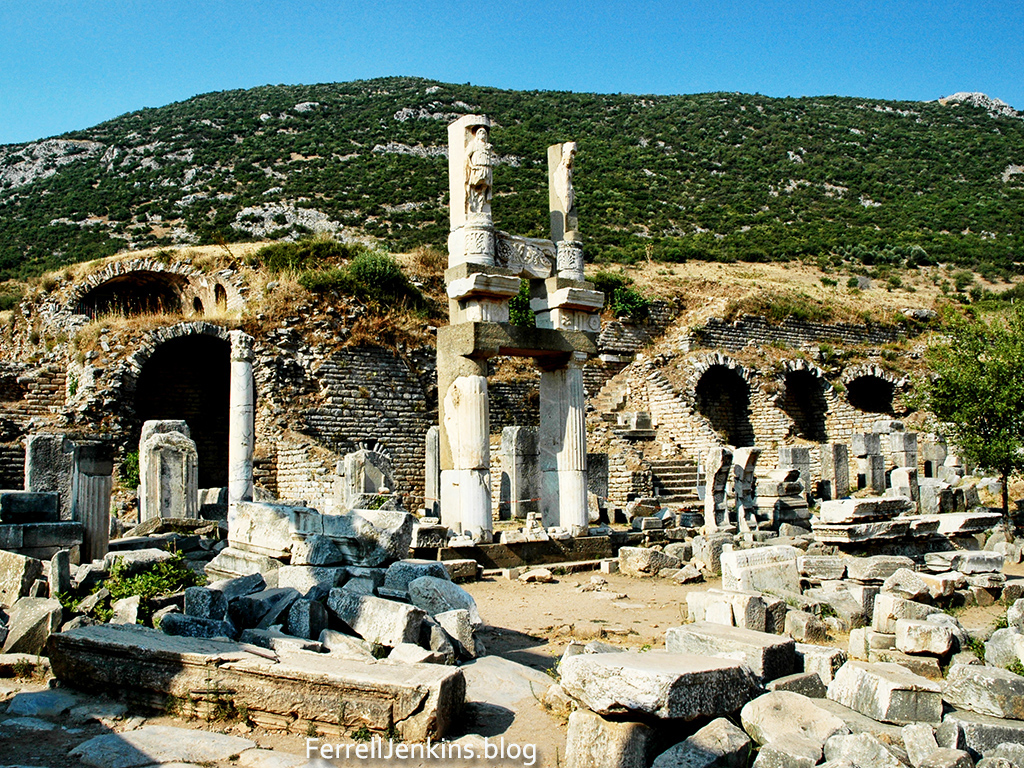

Domitian Square at Ephesus. Some writers refer to this area where the temple stood as the temple of the Flavian Emperors. This would include Vespasian, Titus, and Domitian. The temple stood on the platform above the arches. The steps to the right of center led to the temple. Photo by Ferrell Jenkins.
A large statue of the emperor stood on the platform. Several scholars hold the more recent view that the head discovered here is that of Titus.
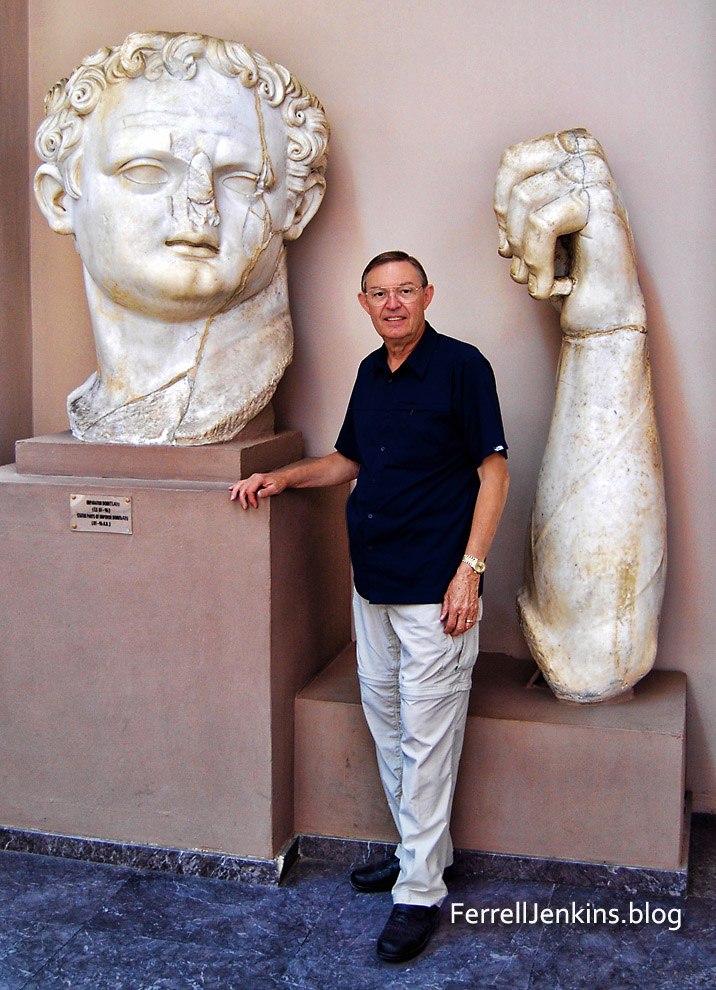

Portions of the larger-than-life statue of Domitian (or Titus) from the temple in Ephesus. Ephesus Museum. Photo: ferrelljenkins.blog.
Smyrna (modern Izmir, Turkey) became a great center for Emperor worship. Out of the Pax Romana (the Roman peace) grew the worship of Dea Roma (the goddess Rome). Smyrna was the first city of Asia to erect a temple to the cult of the city of Rome in 195 B.C. In 26 B.C., during the early imperial period, eleven cities of Asia were competing for the right to build a temple of Tiberias and thus become the neokoros (temple warden) for the Roman Imperial cult. Rome decided in favor of Smyrna in recognition of her long loyalty (Tacitus Annals Iv. 55.56). Smyrna won the title of “First of Asia” (found on coins) and was thrice named “Temple Warden” (Cosmades, Thomas. Nothing Beside Remains, 1964. 26).
During the reign of the emperor Trajan (A.D. 98-117), Ignatius of Antioch passed through Smyrna on his way to execution in Rome. While at Troas he wrote letters to several churches including The Epistle of Ignatius to the Smymaeans, and an epistle to Polycarp (The Ante-Nicene Fathers).
Polycarp, a leader in the church at Smyrna, was martyred by the Romans in about A.D. 156. He was arrested and ordered to say Lord Caesar” and to offer incense to the image of the Emperor Antonius Pius (A.D. 138–161). Upon refusing to do so, Polycarp was then asked to swear by the fortune of the emperor, to
deny Christ and to denounce the atheists (Christians). He was sentenced to death by burning because he would not comply with the wishes of the authorities. He is remembered for his offer to teach the
Roman soldiers, and for saying “Eighty and six years have I served Him, and He never did me any injury; how then can I blaspheme my King and my Saviour?” Yamauchi says about 10 other Christians were martyred in the city’s stadium at the same time (The Archaeology of New Testament Cities in Western Asia Minor, p. 61).

Polycarp of Smyrna was put to death during the reign of Antonius Pius in about A.D. 156. Powerpoint slide: ferrelljenkins.blog.
In Izmir, Turkey, the modern counterpart of ancient Smyrna, we find the Polycarp church. There a large piece of art illustrates what we know about his death.
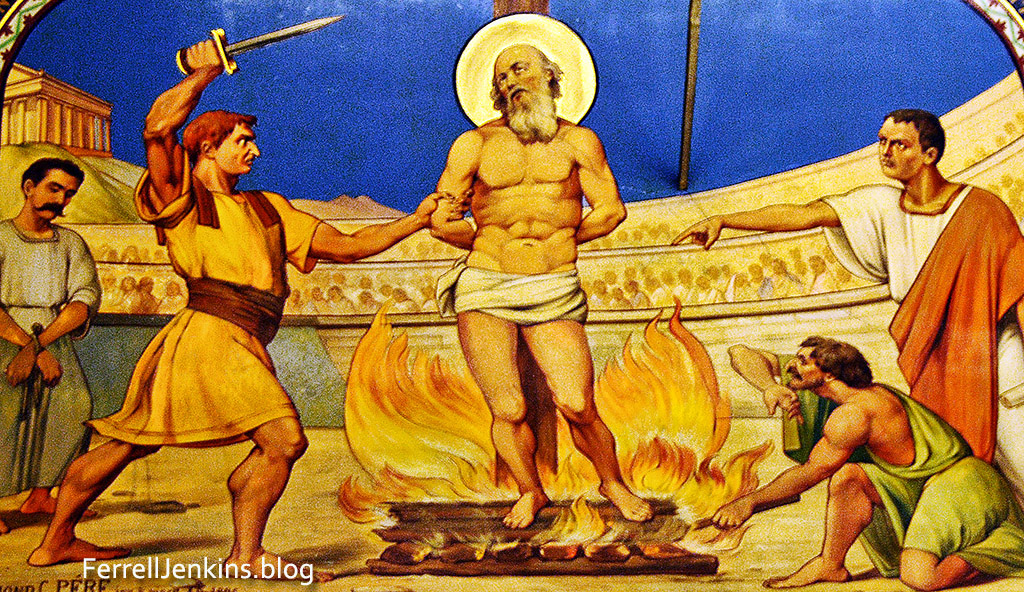

Artist rendition of the martyrdom of Polycarp in the city stadium displayed in the Polycarp church in Izmir. Photo by Ferrell Jenkins.
The letter to the church at Pergamum names a Christian by the name of Antipas who was killed (Rev. 2:13). After the close of the New Testament we find other references to followers of Christ who were martyred at the hands of the Romans.
From the writings of Pliny, governor of Pontus, to the emperor Trajan we learn that the same procedure was practiced by the authorities before they killed Christians. See our article with more photos here.
Numerous illustrations could be used from other cities, but I will leave the subject here. The situation described in the book of Revelation fits perfectly with what we learn when we read the history of the area and visit the ruins of the ancient cities named in the book.
The term autokrator (= English, autokrat) is used of the Roman emperors on coins and inscriptions. Domitian styled himself Master and God. Two inscriptions found at Jerash, Jordan, in 1974 describe Domitian as son of the divine (theou) Vespasian. Domitian’s name is erased from both inscriptions as it is on many other inscriptions indicating that he is of damnable memory. After the death of Domitian the Roman Senate issued a damnatio memoriae (of damnable memory) and his name was erased from many monuments throughout the Empire. I have examples of this from Ephesus, Smynra, Thyatira, and other places. (See Franz, Gordon. “The King and I: The Apostle John and Emperor Domitian.” Bible and Spade 12.2 (1999): 44. Print.
Above I mentions my Studies in the Book of Revelation. There I list several believers who were martyred during the reign of various Roman emperors (pp. 79-81).
Our lesson from all of this is to be loyal to Christ no matter what the threat may be.
















You must be logged in to post a comment.